Audita blog - 18 OCT 2024
What are MEV Bots: Security Measures and MEV Explained
MEV has been shaping the crypto ecosystem as we know it, lurking in the background and capturing every opportunity, the average MEV bot allegedly making north of $300K per month.
MEV is both a source of fascination and controversy within the crypto community. This article will demystify MEV bots, exploring their impact, the debates surrounding their use in decentralized finance (DeFi) and touch upon security-relevant aspects of MEV.
What are MEV Bots?
MEV stands for Maximum Extractable Value. MEV Bots are essentially programs designed to detect any price discrepancies and opportunities to extract value from a liquidity pool, a trade, or to manipulate transaction ordering in the blockchain to maximize profit.
These bots operate by monitoring the mempool for pending transactions, allowing them to execute strategies such as arbitrage, front-running, back-running, sandwich attacks and more.
MEV Bots - Transaction Ordering and Sandwich Attacks
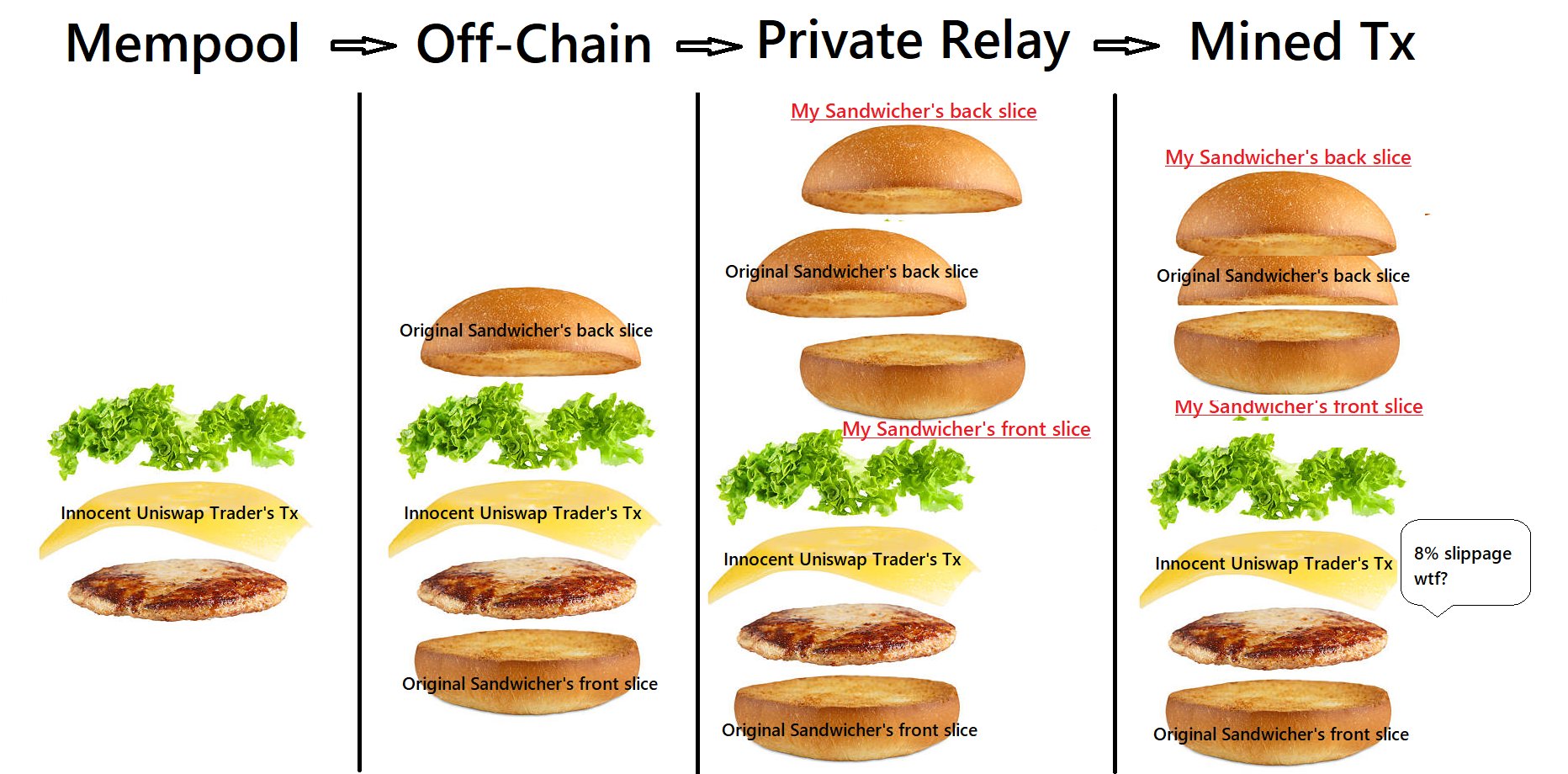
All transactions queue in the mempool waiting to be executed. In the days before the Merge, miners could spot pending transactions and decide to swoop in and change the course of execution, adding their own transaction in between.
For example, if they spotted a high value transaction that will shift the market, they could jump ahead of it with their own transaction and benefit from the price change. This is front running MEV.
Back running is doing the same, only positioning their transaction after a transaction that creates a significant price change, benefitting from price discrepancies caused by transaction 1.
Doing both front running and back running is called a sandwich attack, as shown below:
Another form of market manipulation through MEV is censorship. Miners could decide to make it more difficult for transactions to be executed by imposing higher fees, or manipulating oracles. Having set up a MEV strategies, censorship helped them secure their profits.
MEV for Arbitrage and Flash Loans
In DeFi, MEV bots leverage flash loans to make profits by executing complex arbitrage strategies within a single blockchain transaction.
Flash loans allow these bots to borrow amounts of funds instantly, without needing any upfront collateral. Then, they can capitalize on price discrepancies across different decentralized exchanges (DEXs) using these funds, and after the profit is secured - repay the borrowed amount in the same transaction.
This mechanism shows the trading power of MEV bots and reduces financial risk, as the transaction either completes successfully with profit or reverts entirely if it fails, ensuring there are no losses. No wonder flash loans have become a critical tool for MEV bots and are widely preferred as a strategy.
MEV and Liquidations
MEV bots play an important role in DeFi by identifying and acting on under-collateralized loans.
When a trader's collateral value drops below a certain threshold, signaling a liquidation, MEV bots monitor platforms like Aave or MakerDAO for such opportunities. When they detect one, the MEV bots can swiftly submit their own liquidation order, often outbidding other transactions by manipulating gas fees to secure a priority position in the transaction queue.
The bot can profit from the liquidation process by seizing the collateral and selling it at market value, thus earning a liquidation fee. Additionally, MEV bots may utilize flash loans to access the necessary capital for executing these liquidations, removing the need for upfront collateral. This maximizes profits for the bot operators and contributes to maintaining liquidity and stability within DeFi, albeit at the potential expense of the traders being liquidated.
Toxic MEV vs Non-Toxic MEV
As we saw in the above liquidations example, MEV bots can be extremely valuable for DeFi.
Users have classified MEV bots into toxic and non-toxic, depending on their impact on the ecosystem.
Toxic MEV
Toxic MEV result in a worse execution of user transactions than what they anticipated. With censorship, for example, the decentralized nature of blockchain applications is put at risk, also falling under toxic strategies.
Blockchain protocols which make efforts to create and use decentralized sequencers such as Metis L2 are going to receive more and more attention in the coming years.
Non-Toxic MEV
Non-toxic MEV do NOT impact users or the integrity of the blockchain negatively. Arbitrage and back running ensure more efficient prices in the market. Without arbitrage, price fluctuations would be higher and more long-lasting.
It's important to note that a non-toxic classification of MEV bots can be very subjective, and each case should be looked at separately.
MEV-Boost
MEV-Boost was designed by Flashbots and the Ethereum Foundation as the MEV solution post-Merge. After Ethereum transitioned to Proof-of-Stake, validators were the ones deciding on transaction sequencing. MEV-Boost is essentially proposer-builder separation. Validators can sell block space to third parties called block builders, who collect and sequence transactions.
It's built as a free, open-source, neutral software aiming to assist the flow of transactions on the Ethereum network. MEV-Boost allows validators to pick the highest paying block offered by builders. Then, builders compete to produce blocks. The validator chooses the highest paying block and proposes it to the network.
MEV-Boost quickly accounted for 90% of the ecosystem.
Our team at Audita aims to foster a secure DeFi ecosystem that protects users from the adverse effects of toxic MEV, promoting fair trading environments.
Building a safer Web3 together, one audited protocol at a time. Reach out to us!
STAY SAFU
Audita's Team